Transforming Global Connectivity with Decentralized Internet Infrastructure
The “Internet” is one of the biggest milestones in the modern era. Can you imagine a single day without internet connectivity? Extremely difficult right? Just like saltless curry! The Internet has made our daily lives easier, as it makes it easier to be up-to-date with news, pay bills, do online work, communicate with your dearest ones, and many more. The modern Internet is highly centralized, and major corporations and governments control vast portions of the infrastructure, access, and data.
This centralization comes with vulnerabilities, such as censorship, surveillance, security risks, and the monopolization of digital services. Owing to the pace of technology, blockchain-powered decentralized Internet is becoming a revolutionary alternative. This article explores various aspects of Internet decentralization, covering real-world examples, technical foundations, implementation, and its potential impact on global connectivity. It also highlights the most anticipated technologies shaping this shift.
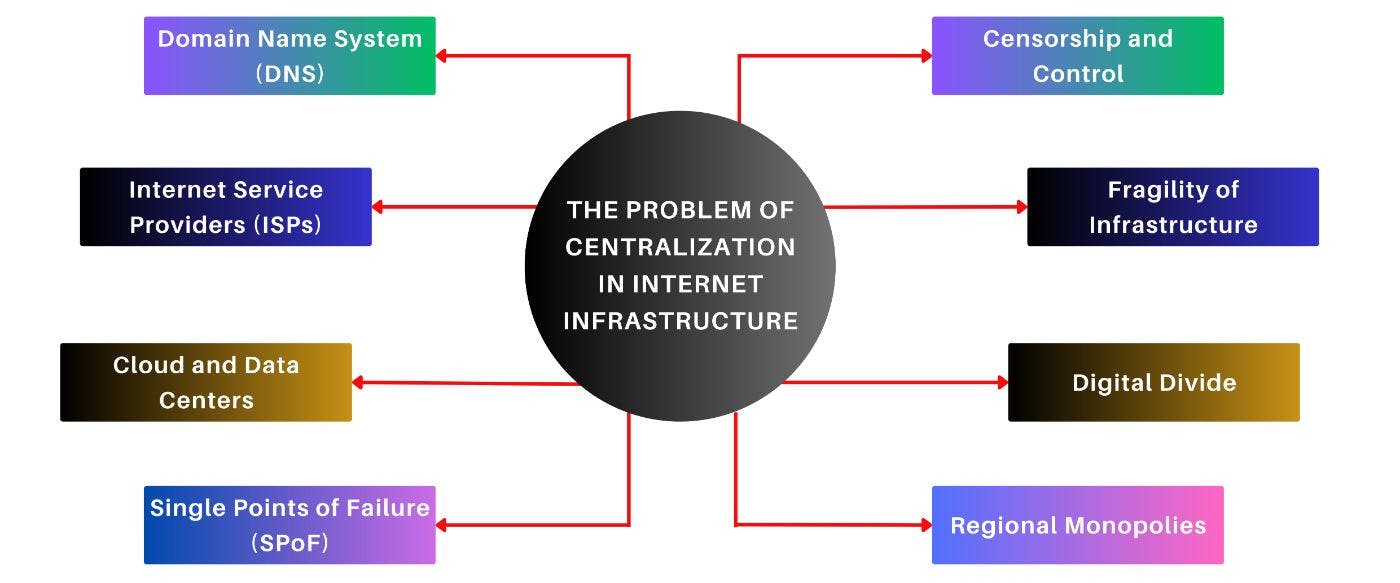
📥The Problem of Centralization in Internet Infrastructure
Let us discuss the most popular Domain Name System (DNS), which is continuously monitored by several key organizations, such as ICANN. It limits diversity in management and sets the stage for a chain of centralized control. This centralization is also applicable to Internet Service Providers (ISPs). ISPs act as gatekeepers with the power to restrict access and to engage in surveillance. This sort of intervention concentrates on controlling our online experiences. The apex of this hierarchy is occupied by major technology giants such as Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, which control the majority of cloud computing and data center services. This concentration of power in the hands of a few raises questions about the Internet’s decentralization and accessibility.
This centralization can trigger notorious single points of failure risks, which makes the system vulnerable to cyberattacks and shutdowns. Centralization also enables censorship, which allows governments to block websites, restrict online freedoms, and control the flow of information. These results often suppress protests and limit access to unbiased content.
The weakness of this centralization makes it vulnerable to disruptions such as hacker attacks and equipment failures. In addition, many areas still cannot access the Internet adequately because it is too expensive to set up. Big Internet companies control whole regions, which makes things worse by driving up prices and making it difficult for many people to afford the Internet. With no real competition, these companies do not have much reason to make things better or to come up with new ideas.
Decentralized Internet
Web3 represents the decentralized Internet, which is expected to be a significant improvement in online communication. The digital world under Web3 allows you to take back authority over your data and digital identity from tech giants. With Web3, people have personal Internet keys for access without outside control. Blockchain technology acts as the foundational structure of this new network-based system, providing complete transparency and unalterable record-keeping capabilities.
If we demand true democracy, even in the digital world, transparency in our processes is essential. Web3 embraces this by using cryptocurrencies as its core currency—digital tokens that serve dual roles in asset valuation, system access, and governance within digital communities. It offers “users access” to digital spaces worldwide through this specific network authorization. All the hype Web3 is getting is not only due to rumors and blind trends but also because of its core value—enhancing privacy standards.
Internet surfing is possible without delivering data points to advertisers through information trails. Just as an invisible cloak lets you choose when to be seen in a crowd, Web3 gives you control over your online presence. The core principle governing a decentralized Internet is its resistance to censorship. Web3 provides mechanisms that guarantee that no one’s voice can be silenced by establishing public forums worldwide that provide equal opportunities for users to share their voices with everyone else. The decentralized Internet exists primarily as a concept but requires further progress to become fully mature. Similar to every innovative system, practical challenges are encountered during the development phase. But, while still evolving, Web3 has the potential to overcome challenges and redefine digital transformation through a more inclusive platform.
Spacecoin: Real-world Example of a Decentralized Internet
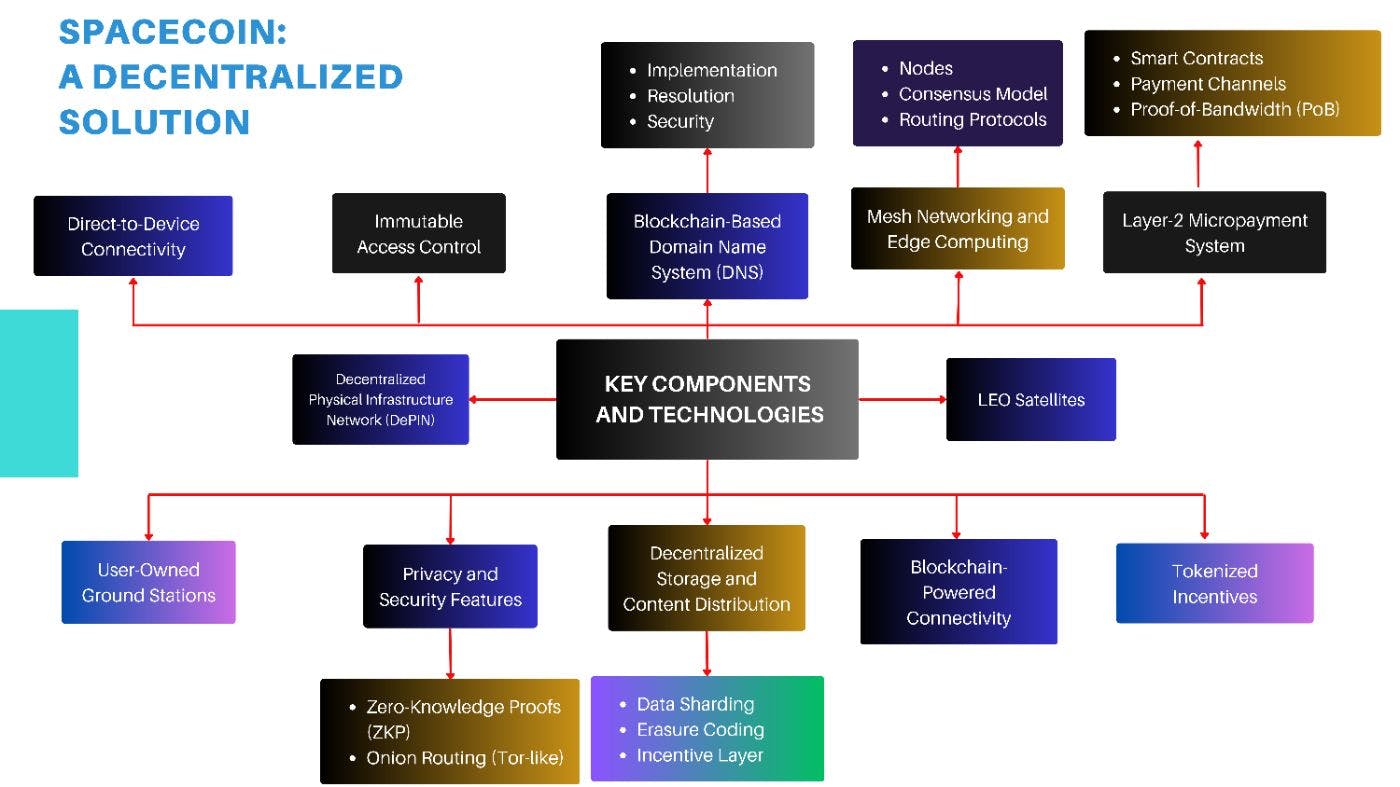
Spacecoin utilizes blockchain technology, decentralized networks, and financial incentives to create an Internet that is autonomous, resistant to censorship, and free from the need for trust between parties. It integrates blockchain technology to create a peer-to-peer space-based decentralized Internet.
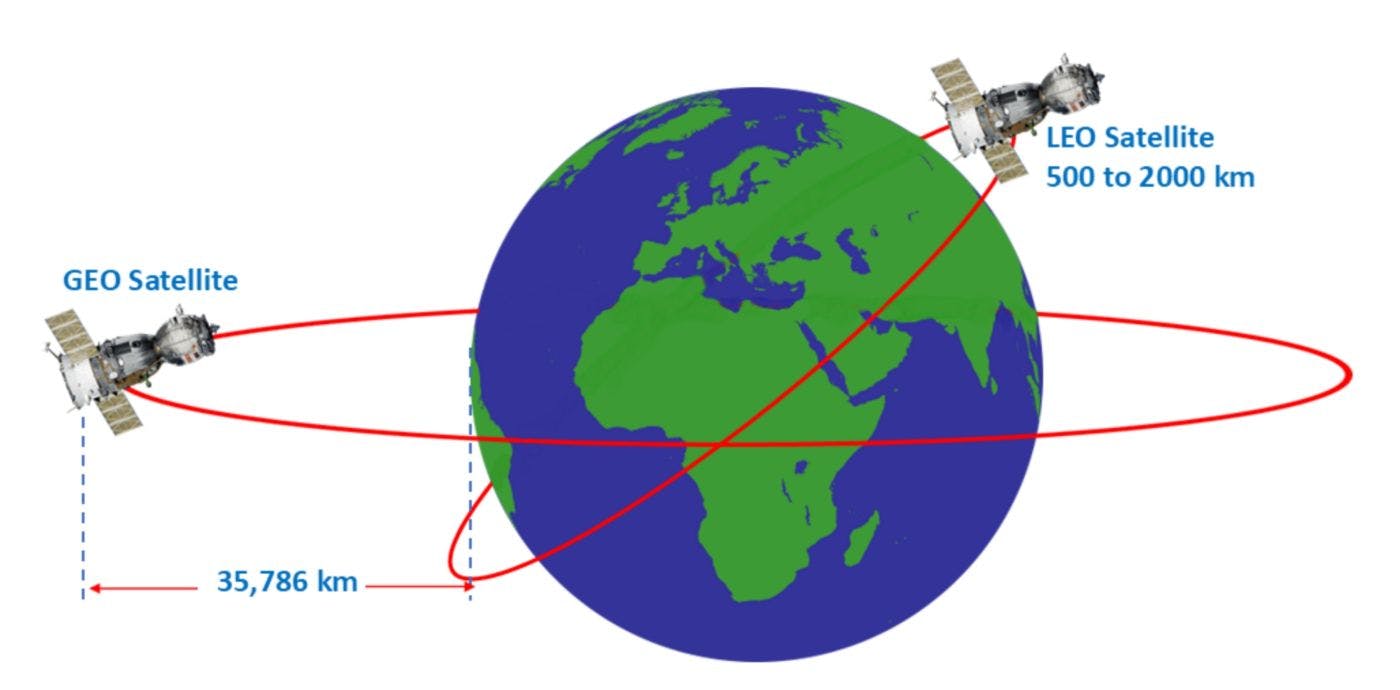
The Spacecoin network operates through decentralized Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, which preserve secure anonymous data transfer beyond central-authority interference. The management of satellite communication networks through Spacecoin operates independently of corporate control while enabling a worldwide community for network administration. Spacecoins operate through LEO satellites, which orbit from 500 to 2000 km above Earth. The location of LEO satellites between 500 and 2000 km dramatically shortens the transmission times against geostationary satellites located at 35,786 km. Linked networks consisting of LEO satellites provide dependable and steady Internet connections by enabling communication between the satellites.
The decentralized DNS (dDNS) from Spacecoin leverages blockchain technology to address the vulnerabilities of traditional domain name systems. The domain registration processes in this system run through smart contracts that work with an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The Spacecoin network depends on peer-operated nodes to authenticate domain connections to keep records unalterable and secure them against DNS hijacking and phishing threats. It establishes its network structure through decentralized principles by allowing individual users to operate nodes that link via wireless capabilities, including LoRaWAN, Wi-Fi Direct, and 5G. Participants can use Spacecoin tokens to engage in a bandwidth-sharing network, where data packet routing is managed through blockchain-encrypted protocols.
Lightning network principles power the second-layer micropayment system, benefiting decentralized Internet service providers and individual users sharing bandwidth resources. Smart contracts execute transactions in real-time, and off-chain payment channels minimize congestion on the blockchain. Participants earn rewards based on the size and quality of bandwidth they provide. The Spacecoin network integrates decentralized storage solutions like IPFS and Arweave, reducing reliance on centralized data centers. By using sharding, data is fragmented, encrypted, and distributed across multiple nodes for security. Erasure coding further enhances data durability and redundancy. Users who host or distribute content are incentivized through a rewards system.
User privacy protection and exceptional security measures are the foundation of Spacecoin’s core architecture. The ZKP technology executes private transactions together with user verification operations. Onion routing is the key security feature of this system because it uses Tor network-like encryption methods to distribute data between multiple network nodes to prevent censorship.
Networking participants enable token rewards through the operation of transmission stations, which helps maintain network stability and distribute internet data. Users access payment incentives via a token reward system. This method creates the conditions that support community-based partnerships.
A Proof-of-Connectivity (PoC) consensus protocol serves as a distinctive system component that rewards any combination of satellites, ground stations, and individual users while maintaining secure information transmission between network components. The system’s authentication of all transactions is ensured through smart contracts that also provide transparency and security.
The project used spacecoin (SPC) tokens to reward participants who donated bandwidth or sustained network nodes to increase engagement and network expansion. Within this network, users protect their services through cryptographic keys that authorize proper individuals while denying unauthorized user access. Through its Spacecoin functionality, the system enables standard 5G smartphone users to connect directly, despite requiring no additional hardware setup. Spacecoins accomplish this objective through 5G Non-Terrestrial Network technology, thus enabling the removal of traditional ground connectivity requirements to distribute Internet services globally.
Spacecoin Transmissions
Each user in the 5G-NTN framework uses a pair of asymmetric keys that link to them only. This communication process depends on two system functions: the “Requester” and the “Transmitter.”
-
When data transportation is required, the requester selects the transmitter from the available options.
-
The transmitter executes the requests by providing the requested information.
-
The transmitter receives confirmation through an acknowledgment or an ACK from the requestor. The transmitter generates an acknowledgment using its private key to prove that it has finished the requested service.
-
After completing their data transfer service, the transmitter submits its receipt to the Spacecoin blockchain to receive a payment through the promised fee. Blockchain escrow from Spacecoin acts as a mechanism to guarantee transmitter payments for their services. Before a request is made, the requester places the Spacecoin tokens into a smart contract escrow, which the transmitter can verify independently. After receipt submission to the blockchain, the promised fee is transferred automatically from the escrow. Spacecoin addresses the lack of ACK submissions from requesters through the implementation of its credit system. A lack of ACKs is unprofitable for requesters because network disconnection damages their interests more than avoiding bill payments.
Transmitters can also report free riders to the network, leading to the collective rejection of unwanted requests.
Key Use Cases of Spacecoin’s Decentralized Internet
Internet censorship should be absent to provide journalists and activists with secure communication access that disengages them from Internet service providers. The network enables users to establish secure communication channels that remain functional even under authoritarian restrictions, which protect the freedom of expression and exchange of information.
Decentralized connectivity helps users find DeFi solutions that allow them to access cryptocurrency assets and complete digital transactions outside of traditional banking networks. The key benefit of decentralized network systems is maintaining uninterrupted messaging during emergencies and preserving network connectivity during natural disasters. Providing backup communication outside traditional earthbound network disruptions can protect human life and support appropriate disaster-management actions.
A decentralized network can be used to safely gain access to dApps, NFT marketplaces, and metaverse platforms when accessed from areas where internet control or infrastructure limitations persist.
Challenges and Future Developments
Spacecoin faces several obstacles and opportunities for its future growth.
-
Governments may resist a decentralized Internet due to concerns over national security and tax implications.
-
The scientific community continues to face challenges in maintaining efficient proof-of-connectivity (PoC) for many users. Further investigation is required to enhance and operate AI-driven PoC systems.
-
Affordable ground station hardware is crucial for mass adoption and requires collaboration with hardware manufacturers and tech firms to make quantum-encrypted ground stations widely accessible.
-
The different aspects of blockchain technology and proof-of-bandwidth (PoB) mining create technical obstacles. The main barrier to blockchain usage arises from time-related scalability issues, along with delays caused during the verification processes. Users face the major obstacle of hardware adoption during participation because they require suitable routers, matching antennas, and computers that many people cannot afford. Energy efficiency is important because the proof of bandwidth mining requires the optimization of energy usage to maintain sustainable and environment-friendly mining operations. The deployment of blockchain and PoB mining technologies requires a solution to the existing challenges for effective and secure execution.
-
Modern satellite technology faces various issues in aerospace applications. Small satellite systems must handle two major space challenges from intense radiation and extreme temperatures because these factors can damage both operations and useful lifespans. To achieve this goal, high-speed data transmission to mobile devices requires the efficient design of an effective compact receiver. Decentralized governance models add operational complexities when merged with traditional “telco operations,” because they combine centralized infrastructure features with distributed control systems. Managing thermal conditions is very important when operating a strong RF amplifier on a small spacecraft because insufficient cooling systems can result in performance failure. The exact positioning of satellites during orbital insertion remains vital because it determines the coverage areas while reducing launch expenses. The aerospace industry faces current problems that demonstrate how effectively innovating, while remaining practical, defines modern aerospace operations.
-
Problems in telecommunications arise from the control mechanisms that limit new ideas and delay responses. The process of securing spectrum licenses from authorities represents an inflexible system that causes both slow deployment times and strict limitations due to official regulatory requirements. All SIM and eSIM activation authentication rests with 3GPP because it operates as the main authority managing the root certificate authority (CA). The security controls implemented by this management system protect standards but also slow down the adaptability of mobile telecommunication systems to new technology and market requirements.
Addressing Telecommunications Challenges
Successful implementation relies on strategic collaboration and technological advancements. Spectrum licensing restrictions can be addressed by partnering with organizations that hold the necessary licenses, accelerating deployment. New Radio Unlicensed (NR-U) technology enhances 5G networks by expanding coverage and optimizing operations across unlicensed spectra. SIM/eSIM activation becomes more efficient with GSMA-certified third-party support, improving compliance management. Security is strengthened through a decentralized root CA oversight entity for SIM and eSIM certification. These approaches help traditional telecommunication systems evolve into faster, more efficient, and adaptable networks.
✅Governance
During the beta stage, governance management falls under the “Spacecoin Foundation, ” which leads the Spacecoin evolution to its complete functional state. The network matures until a decentralized model takes over decision-making among users. The production governance framework uses a voting system that allows Spacecoin holders to assess every proposed protocol upgrade through transparent collective processes for future change. Decentralized governance has replaced centralized governance to improve community engagement for sustained network success and adaptiveness.
📥The Future
So, what’s the next? Although future forward technologies, such as Spacecoin, are already in place, the world must be prepared to combat potential challenges to achieve full-fledged Internet decentralization. Adoption and technical literacy can be major factors, as technology remains experimental.
🚀AI-Based Traffic Optimization
The dynamic management of data flow and congestion reduction are major challenges in optimizing network performance. We believe that machine-learning algorithms play a crucial role in addressing these issues. Real-time adaptive bandwidth management with smart routing systems optimizes transmission performance through efficient traffic-minimized latency rates and decreased packet failure rates. The predictive analysis of “Artificial Intelligence-powered models” reviews the historical traffic patterns before predicting future congestion to enable preventive alterations. Decentralized protocol integration with AI-driven traffic optimization enables efficient peer-to-peer network data flow.
🚀Quantum Encryption and Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
As quantum computing advances, traditional cryptographic methods face severe challenges owing to their vulnerability to quantum attacks. Bitcoin itself may not be immune to quantum-computer-based attacks. The quantum-key distribution protocol in quantum encryption protects communication through guaranteed encryption keys, intercepts, and decryption resistance. Digital assets receive security through lattice and hash-based algorithms in quantum-resistant cryptography, which protects quantum decryption. Blockchain integration and decentralized infrastructure work together to secure data, because they remove single points that can cause failure.
Several entities, including governments, should develop future-oriented security systems to harness this cryptographic transformation. The development of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) has established itself as a necessary investigative field for building cryptographic systems that defend against quantum and classical computer-based attacks. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) created PQC algorithm standards to establish interoperable and adopted solutions. Modern information security technology uses hybrid system designs that merge classical algorithms with quantum-safe methods to provide short-term defenses against current system weaknesses and future quantum computing threats. Researchers are working at higher speeds to create quantum-safe cryptographic solutions through the quantum-era approach because they want to preserve information secrecy and authenticity in today’s advanced digital networks.
🚀The Multi-Planetary Internet and Verifying Location with Proof of Location (PoL)
As humanity stretches its reach beyond Earth, the dream of a connected solar system is no longer science fiction; it is a practical necessity. Can you imagine a future where astronauts on Mars video-call their families on Earth or lunar mining operations sync data with mission control in real time? Users can expect this promise to arise from a multiplanetary Internet, which uses satellite relays together with delay-tolerant networking (DTN) protocols to connect different planets.
The DTN system functions as a waiting patient courier that stores data when network disruptions occur before it safely transfers the data once the connections become stable. This is the ultimate “wait-and-send” protocol built for the unpredictability of space. A method is required to guarantee that “cosmic hackers” cannot intercept interplanetary signals 😁. Enter PoL—a digital “passport”–for devices. Picture a rover on Europa transmitting data; PoL cryptographically confirms that it is actually on Jupiter’s moon and not a spoofed signal from the Earth. This is not just about security; it is also about trust. By verifying locations, PoL optimizes supply chains for space habitats (no lost shipments to the wrong asteroid!) and locks down the communication between bases. It’s like a universal “trust but verify” handshake for the cosmos.
🚀Non-VPNs and the Metaverse
Traditional VPNs? They are so… Earthbound. In space, latency is an enemy, and centralized servers are bottlenecks. Non-VPNs transform network operations by enabling the use of different methods. Instead of routing data through crowded terrestrial networks, non-VPNs create direct encrypted “tunnels” between satellites, ships, and bases. Let us imagine two astronauts on opposite sides of the Moon with a private chat via laser links: no middlemen, and no lag. This development represents a cybersecurity transformation that simultaneously boosts speed while defending critical missions from listeners and allowing nations and corporate entities to preserve control over their information.
Things might grow wildly based on the combination of metaverse technology with this modern concept. Non-VPNs serve as the infrastructure that enables engineers from Earth to work in real-time with Martian colonists through a shared virtual world using holographic blueprints for future habitat designs. AI systems would model the logistics of asteroid mining, whereas blockchain-protected digital replicas of spacecraft components guarantee authenticity over vast distances. Gamers may even battle aliens in zero-gravity VR arenas hosted on orbital servers. AI digital agents perform asteroid mining logistics simulations, and blockchain-encoded digital components ensure authenticity across interstellar distances. Together, these innovations sketch a future where the lines between planets and pixels blur, a universe where connectivity is not limited by geography, physics, or imagination.
Conclusion
The decentralized Internet marks a new era in global connectivity. This change represents more than new technology because it promises complete online relationship remodeling. The digital world can become accessible to everyone while providing enhanced security through this system. Spacecoin is a project that demonstrates an Internet design belonging to its users as the central concept. In the future, censorship could fade, personal data sovereignty could be fully realized, and humanity could connect not just across Earth but even to distant worlds.
The forward path encounters many obstacles in this future. The transition from current centralized information systems to decentralized management does not materialize in a single instant. The progression toward this future combines revolutionary technology with well-thought-out management principles and an improved public understanding of decentralization processes. Success will require collaboration across countries, industries, and disciplines as well as a steadfast commitment to ethical development that prioritizes user rights above all else. Our vision involves developing multiple planetary connection networks that quantum encryption can protect.
In addition, immersive metaverse environments should be developed because the Internet has always sought to integrate people with data. The decentralized Internet presents a new phase of human connection that allows freedom alongside social connections. This upcoming route presents multiple bends but still holds its worth in terms of exploration. The upcoming “Global Internet” could serve users by transforming into an empowering network free from governance that connects all people. The path to progress requires both inventive motivation and security-minded principles to create a unified community across geographical limitations. Modern society determines the direction and expansion of the Internet as digital networks continue to grow.